 KYOCERA Corporation (Headquarters: Kyoto, Japan; President: Hideo Tanimoto; hereinafter "KYOCERA"), a developer, manufacturer and marketer of solar power systems, and Hanzo First Applied Materials (Headquarters: Anzhou, Zhejiang Province, China; Chairman: Hanzo First Applied Materials Co. On August 1, 2012, Kyocera Corporation ("Kyocera") and First Technologies Inc. ("First") signed a basic agreement to license Kyocera's patented technologies related to encapsulation materials for solar cell modules to First, and to jointly develop new encapsulation materials.
KYOCERA Corporation (Headquarters: Kyoto, Japan; President: Hideo Tanimoto; hereinafter "KYOCERA"), a developer, manufacturer and marketer of solar power systems, and Hanzo First Applied Materials (Headquarters: Anzhou, Zhejiang Province, China; Chairman: Hanzo First Applied Materials Co. On August 1, 2012, Kyocera Corporation ("Kyocera") and First Technologies Inc. ("First") signed a basic agreement to license Kyocera's patented technologies related to encapsulation materials for solar cell modules to First, and to jointly develop new encapsulation materials.
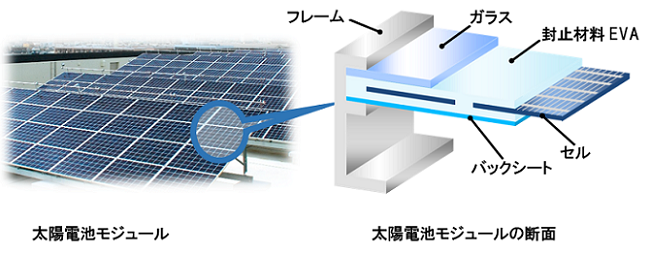
What are encapsulation materials for solar cell modules?
The encapsulation material of a solar cell module is a component that holds the solar cell and protects the solar cell from moisture ingress and other external environmental influences by bonding the glass on the surface and the backsheet on the back side.
Normally, solar cell modules are subject to stresses such as ultraviolet light, humidity, and heat, which generate acid in the encapsulating material made of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), which causes the electrodes of the solar cell to degrade, causing the solar cell module itself to deteriorate. Kyocera's patented technology suppresses the formation of acid in EVA and reduces the degradation of solar cell modules, thus enabling Kyocera's solar cell modules to achieve high long-term reliability.
Kyocera began research and development of solar cells in 1975, and over the course of more than 45 years of research and development, Kyocera has developed technologies related to the long-term reliability of its products.
On the other hand, First entered the solar business in 2003 and has been engaged in the research, development and manufacture of encapsulation materials for solar cell modules and other applications. In 2019, First will be the world's leading manufacturer of encapsulation materials for solar cell modules, with a 50% share of the global market.
Since 2018, the two companies have built a cooperative structure and accumulated manufacturing technology through First's contract manufacturing of Kyocera's "encapsulation materials" for solar cell modules.
The two companies are also working on multifaceted solutions to environmental issues. For example, in addition to promoting the widespread use of solar cell modules to promote RE100, there is also a need to extend the service life of solar cell modules to reduce the total amount of waste from the perspective of the SDGs, Goal 11*. Against this backdrop, the two companies believe that further development of technologies for solar cell modules is urgently needed, and Kyocera has recently licensed its patented technology in the area of long-term reliability to First Solar, and Kyocera and First Solar have agreed to work together to further improve long-term reliability based on this technology. The two companies have reached a basic agreement to develop a new encapsulation material for solar cell modules.
Through the development and widespread use of new encapsulation materials, the two companies will ensure higher reliability of solar cell modules, which will increase the lifetime power generation of solar cell modules and contribute to the reduction of the total amount of waste of solar cell modules in the future. The two companies will continue to promote RE100 and the SDGs through these initiatives.
Going forward, Kyocera and First will continue to contribute to the realization of a low-carbon society by promoting efforts to address global environmental issues and contribute to the development of a sustainable society.
Goal11 More specifically, "11.6.1 Proportion of urban solid waste regularly collected and properly disposed of (by city) out of the total amount of urban solid waste generated (by city). adequate final discharge out of total urban solid waste generated, by cities
www.kyocera.co.jp



































































































